What is Data Warehouse?
What is a Data Warehouse?
A Data Warehouse (DW) is a relational database that is designed for query and analysis rather than transaction processing. It includes historical data derived from transaction data from single and multiple sources.
A Data Warehouse provides integrated, enterprise-wide, historical data and focuses on providing support for decision-makers for data modeling and analysis.
It is not used for daily operations and transaction processing but used for making decisions.
A Data Warehouse can be viewed as a data system with the following attributes:
- It is a database designed for investigative tasks, using data from various applications.
- It supports a relatively small number of clients with relatively long interactions.
- It includes current and historical data to provide a historical perspective of information.
- Its usage is read-intensive.
- It contains a few large tables.
"Data Warehouse is a subject-oriented, integrated, time-variant and non volatile store of information in support of management's decisions."
Characteristics of Data Warehouse
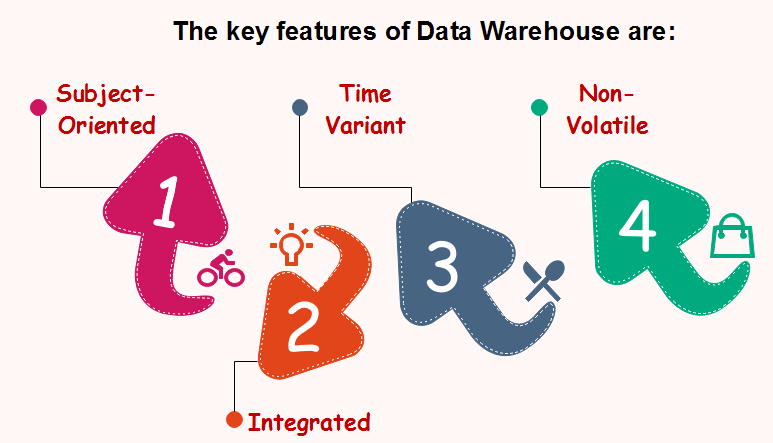
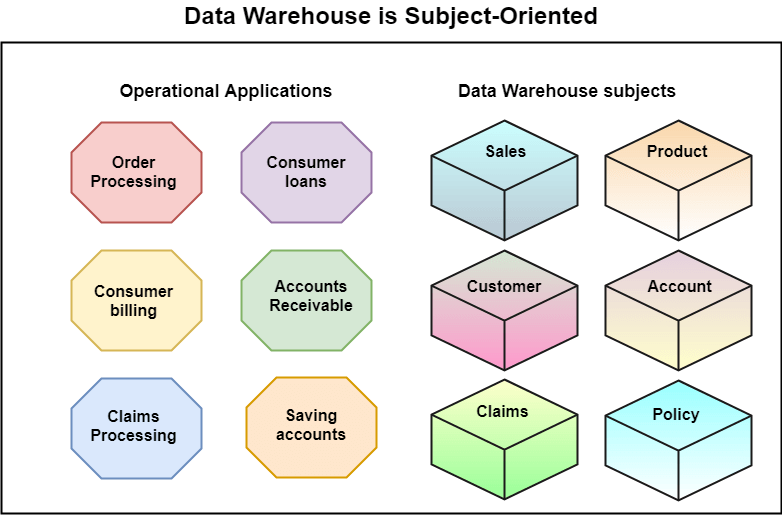
Subject-Oriented
A data warehouse target on the modeling and analysis of data for decision-makers. Therefore, data warehouses typically provide a concise and straightforward view around a particular subject, such as customer, product, or sales, instead of the global organization's ongoing operations. This is done by excluding data that are not useful concerning the subject and including all data needed by the users to understand the subject.
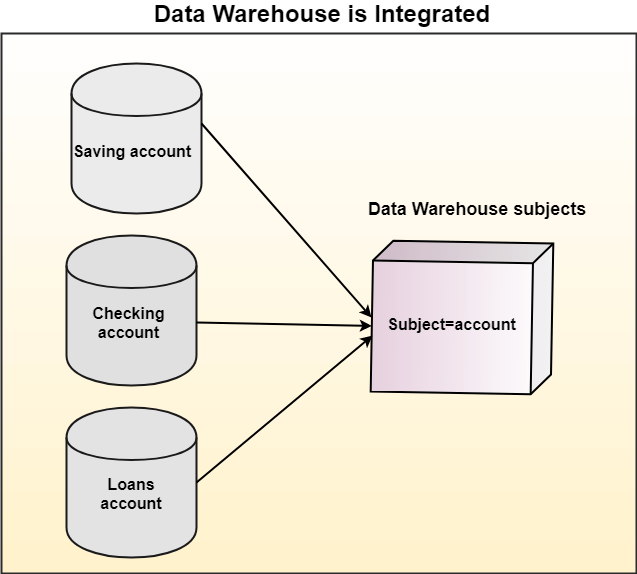
Integrated
A data warehouse integrates various heterogeneous data sources like RDBMS, flat files, and online transaction records. It requires performing data cleaning and integration during data warehousing to ensure consistency in naming conventions, attributes types, etc., among different data sources.
Time-Variant
Historical information is kept in a data warehouse. For example, one can retrieve files from 3 months, 6 months, 12 months, or even previous data from a data warehouse. These variations with a transactions system, where often only the most current file is kept.
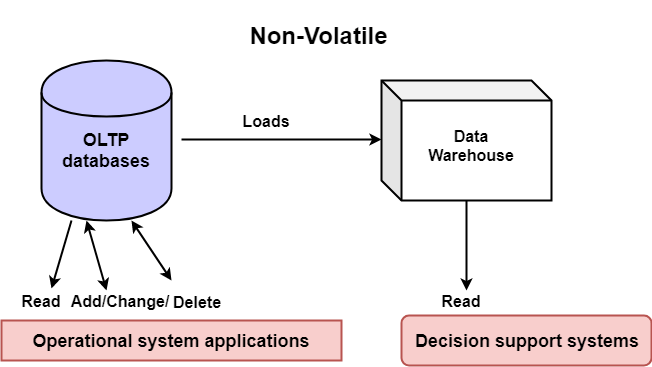
Non-Volatile
The data warehouse is a physically separate data storage, which is transformed from the source operational RDBMS. The operational updates of data do not occur in the data warehouse, i.e., update, insert, and delete operations are not performed. It usually requires only two procedures in data accessing: Initial loading of data and access to data. Therefore, the DW does not require transaction processing, recovery, and concurrency capabilities, which allows for substantial speedup of data retrieval. Non-Volatile defines that once entered into the warehouse, and data should not change.
History of Data Warehouse
The idea of data warehousing came to the late 1980's when IBM researchers Barry Devlin and Paul Murphy established the "Business Data Warehouse."
In essence, the data warehousing idea was planned to support an architectural model for the flow of information from the operational system to decisional support environments. The concept attempt to address the various problems associated with the flow, mainly the high costs associated with it.
In the absence of data warehousing architecture, a vast amount of space was required to support multiple decision support environments. In large corporations, it was ordinary for various decision support environments to operate independently.
Goals of Data Warehousing
- To help reporting as well as analysis
- Maintain the organization's historical information
- Be the foundation for decision making.
Need for Data Warehouse
Data Warehouse is needed for the following reasons:
- 1) Business User: Business users require a data warehouse to view summarized data from the past. Since these people are non-technical, the data may be presented to them in an elementary form.
- 2) Store historical data: Data Warehouse is required to store the time variable data from the past. This input is made to be used for various purposes.
- 3) Make strategic decisions: Some strategies may be depending upon the data in the data warehouse. So, data warehouse contributes to making strategic decisions.
- 4) For data consistency and quality: Bringing the data from different sources at a commonplace, the user can effectively undertake to bring the uniformity and consistency in data.
- 5) High response time: Data warehouse has to be ready for somewhat unexpected loads and types of queries, which demands a significant degree of flexibility and quick response time.
Benefits of Data Warehouse
- Understand business trends and make better forecasting decisions.
- Data Warehouses are designed to perform well enormous amounts of data.
- The structure of data warehouses is more accessible for end-users to navigate, understand, and query.
- Queries that would be complex in many normalized databases could be easier to build and maintain in data warehouses.
- Data warehousing is an efficient method to manage demand for lots of information from lots of users.
- Data warehousing provide the capabilities to analyze a large amount of historical data.
| Database | Data Warehouse |
|---|---|
| 1. It is used for Online Transactional Processing (OLTP) but can be used for other objectives such as Data Warehousing. This records the data from the clients for history. | 1. It is used for Online Analytical Processing (OLAP). This reads the historical information for the customers for business decisions. |
| 2. The tables and joins are complicated since they are normalized for RDBMS. This is done to reduce redundant files and to save storage space. | 2. The tables and joins are accessible since they are de-normalized. This is done to minimize the response time for analytical queries. |
| 3. Data is dynamic | 3. Data is largely static |
| 4. Entity: Relational modeling procedures are used for RDBMS database design. | 4. Data: Modeling approach are used for the Data Warehouse design. |
| 5. Optimized for write operations. | 5. Optimized for read operations. |
| 6. Performance is low for analysis queries. | 6. High performance for analytical queries. |
| 7. The database is the place where the data is taken as a base and managed to get available fast and efficient access. | 7. Data Warehouse is the place where the application data is handled for analysis and reporting objectives. |
Comments
Post a Comment